The Ultimate Guide to Implementing Dynamic Sitemaps
In today’s fast-moving digital world, keeping your website content fresh, organized, and visible to search engines is more critical than ever. One of the most effective — yet often overlooked — ways to achieve this is by implementing dynamic sitemaps.
Whether you’re running an e-commerce store with thousands of products, a blog that publishes daily, or a content-heavy platform, dynamic sitemaps can be a game-changer for your SEO and site performance. In this guide, we’ll break down what dynamic sitemaps are, why they matter, and how you can implement them step by step.
🔎 What is a Dynamic Sitemap?
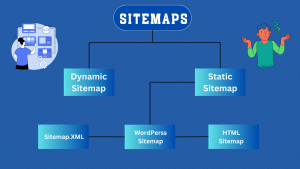
A dynamic sitemap is an XML file that updates automatically whenever content is added, updated, or removed from your website. Unlike static sitemaps, which must be manually updated, dynamic sitemaps stay current without requiring ongoing maintenance.
Dynamic sitemaps are particularly useful for:
-
Large websites with frequently changing content
-
E-commerce platforms with product inventory changes
-
News or blog websites with daily updates
-
Websites with user-generated content
By using a dynamic sitemap, you ensure that search engines like Google, Bing, and others can always access the most recent version of your site’s structure — improving crawl efficiency and visibility.
🚀 Benefits of Using Dynamic Sitemaps
Before diving into the implementation, here’s why dynamic sitemaps are worth the effort:
-
Improved SEO: Keeps your site indexed efficiently by providing real-time updates to search engines.
-
Automation: No need to manually update your sitemap every time new content is added.
-
Better Crawl Budget: Search engines can focus on crawling new or updated content instead of wasting resources on unchanged pages.
-
Error Reduction: Minimizes the chance of sitemap errors or outdated links.
🛠️ Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Dynamic Sitemaps
Let’s walk through how to create and implement a dynamic sitemap for your website. We’ll cover both CMS-based and custom-coded solutions.
Step 1: Understand Your Website Structure
Start by mapping out your content hierarchy:
-
What types of content are published frequently (e.g., blog posts, products, pages)?
-
Are there different content types that need separate sitemaps?
-
How many pages are on your site?
For large websites, it’s best to create segmented sitemaps (e.g., one for blog posts, one for products) and submit them in a sitemap index.
Step 2: Choose Your Approach
Your implementation method will depend on your tech stack. There are typically three ways to build dynamic sitemaps:
✅ CMS-Based (WordPress, Shopify, etc.)
Most modern content management systems offer plugins or built-in features.
-
WordPress: Use plugins like Yoast SEO, Rank Math, or All in One SEO. These generate dynamic sitemaps automatically and update them as your content changes.
-
Shopify: Generates a dynamic sitemap out of the box. Access it at
yourstore.com/sitemap.xml. -
Wix / Squarespace: Also auto-generate and manage sitemaps with no manual work needed.
✅ Framework-Based (React, Next.js, Laravel, etc.)
If you’re using a modern JavaScript or backend framework, you can generate sitemaps dynamically using middleware or build-time scripts.
For example, in Next.js:
-
Use
getServerSidePropsorgetStaticPropsto fetch routes dynamically -
Create a route like
/sitemap.xmlthat returns XML content with proper headers -
Regenerate the sitemap when deploying or on a schedule
✅ Custom Sites
If you have a fully custom-coded site, you’ll need to build the sitemap logic yourself:
-
Query your database for all published URLs
-
Format the results in XML format
-
Serve the sitemap dynamically via a URL (e.g.,
/sitemap.xml) -
Automate the update process using cron jobs or webhooks
Step 3: Generate XML Sitemap Content
Here’s a basic structure of an XML sitemap:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<url>
<loc>https://example.com/page-1</loc>
<lastmod>2025-10-15</lastmod>
<changefreq>weekly</changefreq>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url>
<!-- Repeat for each URL -->
</urlset>
Use server-side code (PHP, Node.js, Python, etc.) to pull data from your database and format it into this structure.
Step 4: Add Sitemap Index (If Needed)
For large websites (over 50,000 URLs), it’s best to break up the sitemap into multiple smaller files.
Create a sitemap index like this:
<sitemapindex xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<sitemap>
<loc>https://example.com/sitemap-posts.xml</loc>
</sitemap>
<sitemap>
<loc>https://example.com/sitemap-products.xml</loc>
</sitemap>
</sitemapindex>
This tells search engines where to find each subset of your full sitemap.
Step 5: Link to Your Sitemap in robots.txt
To help search engines discover your sitemap, include a reference in your robots.txt file:
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml
Step 6: Submit to Google Search Console
Even though search engines can find your sitemap via robots.txt, manually submitting it can speed up the crawling process.
-
Go to Google Search Console
-
Select your property
-
Navigate to Index > Sitemaps
-
Enter your sitemap URL and click Submit
Repeat the process for Bing Webmaster Tools if needed.
Step 7: Set Up Automation and Monitoring
To ensure everything runs smoothly:
-
Automate sitemap regeneration (via deploy hooks, cron jobs, or CMS triggers)
-
Monitor Google Search Console for crawl errors or warnings
-
Validate your sitemap using Google’s sitemap testing tool
❓ FAQs About Dynamic Sitemaps
1. Do I still need a sitemap if my website is small?
While not mandatory, even small sites benefit from having a sitemap. It helps search engines discover your content faster, especially if your internal linking isn’t perfect.
2. What’s the difference between XML and HTML sitemaps?
-
XML sitemaps are for search engines
-
HTML sitemaps are for users, often included in the footer for easy navigation
For SEO, focus on XML sitemaps. For UX, an HTML sitemap can still be helpful.
3. How often should a sitemap update?
With dynamic sitemaps, updates happen automatically when content changes. For static sites, update your sitemap any time a new page is added or removed.
4. Can a sitemap improve my rankings?
A sitemap doesn’t directly affect rankings, but it improves crawl efficiency, which can help new content get indexed faster and more reliably.
5. What happens if my sitemap has errors?
Google Search Console will flag issues like broken links or unreachable URLs. Fix them quickly to avoid indexing problems.
✅ Final Thoughts
Implementing a dynamic sitemap is one of the smartest technical SEO moves you can make, especially for growing websites with lots of content. It ensures that your site stays in sync with search engine crawlers, improves discoverability, and reduces the risk of outdated or missed pages.
Whether you’re using WordPress, Shopify, a modern JavaScript framework, or building from scratch, there’s a dynamic sitemap solution for you. Invest the time to set it up correctly, automate it, and keep it monitored — and your SEO will thank you.
Need help implementing a dynamic sitemap on your platform? Drop a comment below or reach out — we’re here to help!