How to Navigate a CMS Back End Without Breaking Your Site
If you’ve ever logged into your website’s CMS and felt a mix of curiosity and fear, you’re not alone. One wrong click can feel like it might undo months of work—or worse, take your site offline entirely. The good news? Navigating a CMS back end doesn’t have to be risky or intimidating.
In this guide, we’ll walk through how to navigate a CMS back end without breaking your site, even if you’re not a developer. Whether you’re using WordPress, Shopify, Webflow, Wix, or another platform, the principles remain largely the same. With the right approach, you can make updates confidently, understand what you’re looking at, and avoid costly mistakes.
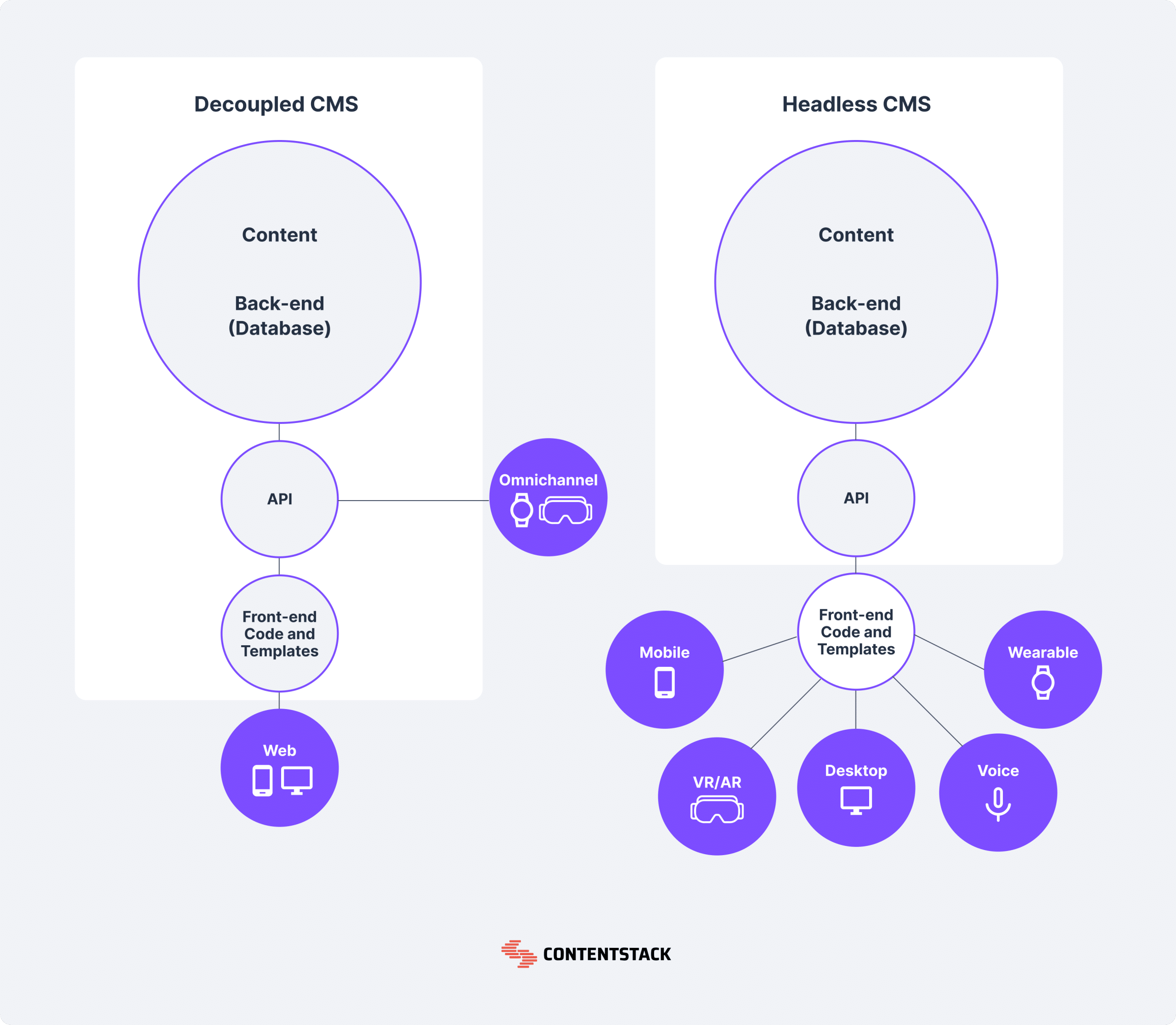
What Is a CMS Back End (and Why It Matters)?
A Content Management System (CMS) back end is the administrative area of your website where content, settings, users, and functionality are managed. This is where you:
-
Edit pages and blog posts
-
Upload images and media
-
Install or manage plugins and extensions
-
Adjust design settings
-
Control user roles and permissions
While the front end is what visitors see, the back end is where the real power—and risk—lives. Knowing how to navigate it safely protects your site’s performance, design, and security.
Before You Start: Essential Safety Rules
Before diving into menus and settings, follow these foundational rules. They alone can prevent most site-breaking issues.
1. Always Have a Backup
Before making any changes, confirm that your site is backed up. Many CMS platforms or hosting providers offer automatic backups, but don’t assume they’re running.
Best practice:
-
Use daily automated backups
-
Confirm you know how to restore one
A backup turns a potential disaster into a minor inconvenience.
2. Use the Right User Role
Not everyone needs full admin access. Editors, authors, and contributors should only have permissions relevant to their tasks.
Why this matters:
Limiting permissions reduces the risk of accidental changes to critical settings.
3. Avoid Peak Traffic Times
If something does go wrong, it’s better for it to happen when fewer users are on your site. Schedule updates during low-traffic hours whenever possible.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Navigate a CMS Back End Without Breaking Your Site

Step 1: Get Familiar with the Dashboard Layout
Most CMS dashboards follow a similar structure:
-
A main navigation menu (usually on the left)
-
A content area in the center
-
Settings or quick actions at the top
Spend time clicking through without changing anything. This “read-only tour” helps you understand what each section controls.
Common sections include:
-
Pages or Posts
-
Media Library
-
Appearance or Design
-
Plugins or Extensions
-
Settings
-
Users
Knowing where things live reduces panic later.
Step 2: Start with Content, Not Settings
If you’re new to a CMS back end, stick to content-related areas first.
Safe places to start:
-
Editing text on existing pages
-
Updating blog posts
-
Replacing images in the media library
Avoid global settings early on. Content changes are usually isolated and reversible.
Pro tip:
Use the “Preview” feature whenever possible before publishing changes.
Step 3: Understand Global vs. Page-Level Changes
One of the most common mistakes is confusing global settings with page-specific edits.
-
Global changes affect the entire site (themes, templates, typography, navigation).
-
Page-level changes affect only one page or post.
Before saving anything, ask yourself:
Is this change meant to affect just this page—or the whole site?
If you’re unsure, pause and research that setting first.
Step 4: Be Cautious with Plugins and Extensions
Plugins can add powerful features—but they’re also a top cause of site issues.
Best practices for plugin management:
-
Install only what you truly need
-
Avoid installing multiple plugins that do the same thing
-
Check compatibility with your CMS version
-
Update plugins one at a time
If something breaks after a plugin update, you’ll know exactly which one caused it.
Step 5: Never Edit Live Code Unless You Know What You’re Doing
Many CMS platforms allow you to edit theme files or custom code directly from the dashboard. This is one of the riskiest areas.
If you see:
-
CSS editors
-
PHP or JavaScript files
-
Theme file editors
…and you’re not confident in what you’re editing, don’t touch them on a live site.
Safer alternatives:
-
Use staging environments
-
Use built-in customization tools
-
Work with a developer for code changes
Step 6: Use Staging or Preview Environments
A staging site is a private copy of your live website where you can test changes safely.
If your hosting provider or CMS offers staging:
-
Test updates there first
-
Review layout, functionality, and performance
-
Push changes live only after confirming everything works
This is one of the most effective ways to navigate a CMS back end without breaking your site.
Step 7: Document What You Change
Keep a simple change log:
-
Date of change
-
What was updated
-
Who made the change
This makes troubleshooting far easier if something goes wrong days or weeks later.
Step 8: Log Out and Check the Front End
After making updates:
-
View your site in an incognito window
-
Check on mobile and desktop
-
Test key functionality (forms, buttons, checkout, navigation)
Sometimes issues don’t appear until you’re logged out.
Common CMS Back End Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced users slip up. Here are mistakes worth actively avoiding:
-
Deleting pages instead of unpublishing them
-
Updating everything at once
-
Ignoring error or warning messages
-
Installing plugins from untrusted sources
-
Making changes without backups
Slow, intentional changes beat rushed updates every time.
FAQs: Navigating a CMS Back End Safely
What is the safest thing to edit in a CMS back end?
Text content, images, and individual blog posts are typically the safest areas to edit, especially when using preview tools.
Can I break my site just by editing a page?
Rarely. Most site-breaking issues come from global settings, plugin conflicts, or code edits—not standard content updates.
Should I update plugins and themes regularly?

Yes, but do it carefully. Update one at a time, check your site afterward, and always have a backup.
What should I do if I break my site?
Stay calm. Restore from your most recent backup, or contact your hosting provider or developer. Most issues are fixable.
Do all CMS platforms work the same way?
While layouts differ, the core concepts—content vs. settings, global vs. local changes, permissions, and backups—apply across platforms.
Final Thoughts: Confidence Comes from Understanding
Learning how to navigate a CMS back end without breaking your site isn’t about memorizing every feature—it’s about understanding what not to touch and how to make changes intentionally.
With backups in place, a clear understanding of your dashboard, and a cautious approach to plugins and settings, you can manage your website confidently—even as a non-technical user.
Your CMS is a powerful tool. When used thoughtfully, it gives you control—not chaos.