Simple Steps to Secure Your Passwords
In today’s digital world, securing your online accounts is more important than ever. Passwords serve as the first line of defense against unauthorized access to personal data, financial information, and sensitive communications. However, with hackers becoming more sophisticated, it’s essential to ensure that your passwords are strong, unique, and well-protected. In this article, we’ll explore simple but effective steps you can take to secure your passwords and protect your online identity.
Why Strong Passwords Matter
Before diving into the specifics of how to secure your passwords, it’s important to understand why strong passwords are crucial. Weak passwords can be easily guessed or cracked by hackers using various techniques such as brute force attacks, social engineering, or exploiting data breaches. A compromised password can lead to identity theft, financial loss, or the exposure of sensitive personal data.
Using strong passwords is an essential practice in safeguarding your online accounts. A strong password is difficult to guess, contains a combination of characters (letters, numbers, symbols), and avoids common patterns. A weak password, on the other hand, may only consist of simple words, phrases, or personal information that hackers can easily guess.
Step 1: Use Unique Passwords for Each Account
One of the most important steps in securing your passwords is ensuring that each one is unique. Reusing passwords across multiple accounts can make it easier for hackers to access all your accounts if one password is compromised. For instance, if you use the same password for your email, online banking, and social media profiles, a hacker who gains access to one account could potentially access all of them.
Why You Should Avoid Password Reuse
Password reuse is a significant security risk because many data breaches involve hackers obtaining a database of passwords from one service. Once a hacker has access to one of your accounts, they may try using the same password to access other accounts, a technique known as “credential stuffing.” To avoid this risk, always create unique passwords for each online account.
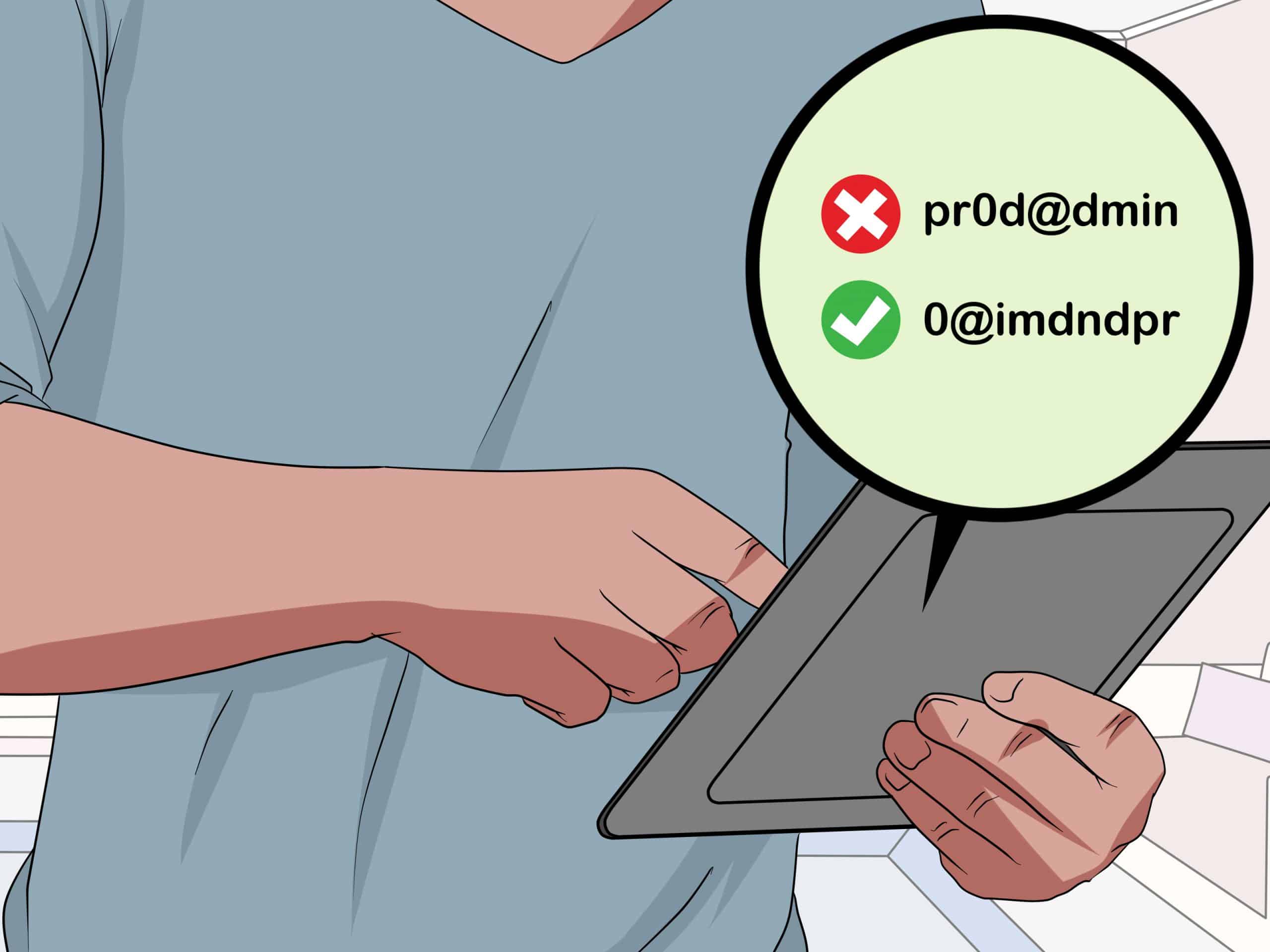
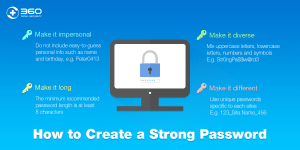
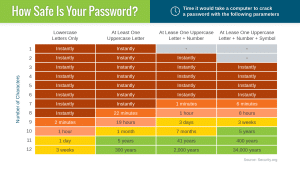
Step 2: Use Complex Passwords
A simple password like “123456” or “password” might be easy to remember, but it’s also incredibly easy for hackers to guess. To create a secure password, it’s important to use a mix of letters (both uppercase and lowercase), numbers, and special characters. The more complex your password, the harder it will be for hackers to crack.
Best Practices for Creating Complex Passwords
- Length: Aim for passwords that are at least 12 to 16 characters long. The longer the password, the more difficult it becomes for hackers to break.
- Character Variety: Include a combination of upper and lower case letters, numbers, and special characters like @, #, and $.
- Avoid Common Words: Avoid using common words, phrases, or easily guessed personal information (like your name, birthdate, or favorite sports team).
- Randomness: A password that is completely random is much harder to crack than one that follows a predictable pattern. Consider using a password generator for this purpose.
Step 3: Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Even the strongest password can be compromised if hackers gain access to your account. To add an extra layer of security, enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible. 2FA requires you to provide an additional verification method (typically a code sent to your phone or email) in addition to your password.
Why 2FA is Essential
2FA significantly improves your account security because even if a hacker obtains your password, they would still need access to your second verification method to successfully log in. This makes it much more difficult for unauthorized users to access your accounts, especially if they don’t have your phone or email.
Step 4: Use a Password Manager
Creating unique, complex passwords for every account can be challenging to manage, especially if you have multiple online accounts. This is where a password manager comes in. A password manager securely stores and organizes your passwords, so you don’t have to remember every single one. With a password manager, you can generate strong passwords, save them, and access them easily when needed.
How Password Managers Work
Password managers encrypt your passwords and store them in a secure vault. All you need to remember is one master password to unlock the vault. Some password managers even have the ability to auto-fill your passwords for websites, making logging in quicker and easier while maintaining security. Popular password managers include LastPass, 1Password, and Bitwarden.
Step 5: Keep Your Passwords Private
Never share your passwords with anyone unless absolutely necessary. Even if someone claims to be from a legitimate company or service, avoid giving them your password directly. Fraudulent attempts to acquire your password are often carried out through phishing attacks, where hackers pretend to be someone you trust, such as a bank or a tech support agent.
Avoiding Phishing Scams
Phishing is one of the most common ways hackers gain access to sensitive information. They often send fake emails or texts that look like they come from trusted sources, asking you to click a link and enter your login credentials. Always double-check the sender’s email address or website URL before clicking on any links. If in doubt, visit the website directly or contact the company for verification.
Step 6: Regularly Update Your Passwords
Even if you create a strong password initially, it’s essential to change your passwords regularly. Regular updates reduce the risk of your accounts being compromised over time, especially if a service you use experiences a data breach.
When to Change Your Passwords
- After a Data Breach: If a service you use experiences a data breach, immediately change your password for that service and any other accounts where you may have reused the same password.
- Every 3–6 Months: Consider changing your passwords periodically (e.g., every 3 to 6 months) to ensure continued security.
- After Suspicious Activity: If you notice any suspicious activity on your accounts, such as unauthorized logins or changes, immediately change your password and enable 2FA.
Step 7: Be Cautious When Using Public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi networks, such as those found in coffee shops or airports, are not secure. Hackers can potentially intercept data transmitted over these networks, including passwords. To protect your accounts while using public Wi-Fi, consider using a virtual private network (VPN), which encrypts your internet traffic and hides your online activities from prying eyes.
Tips for Using Public Wi-Fi Safely
- Avoid Logging Into Sensitive Accounts: If possible, avoid logging into accounts that contain sensitive information, like online banking, while using public Wi-Fi.
- Use HTTPS: When browsing, make sure the website uses HTTPS (the “s” stands for secure) to ensure your data is encrypted during transmission.
Conclusion
Securing your passwords is an essential step in protecting your online accounts and personal information. By following these simple yet effective steps—such as using unique, complex passwords, enabling 2FA, using a password manager, and avoiding phishing scams—you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to cyberattacks. Remember, the effort you put into securing your passwords today can save you from major headaches and losses in the future. Stay vigilant, and prioritize your online security!