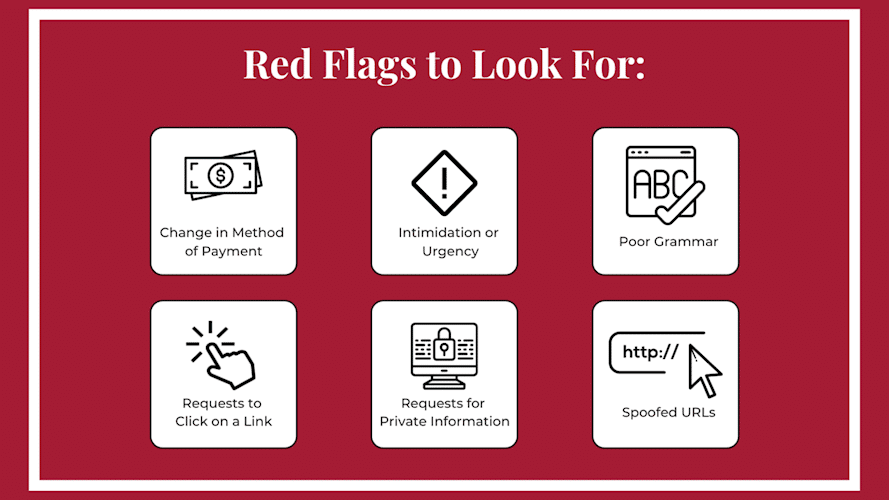
Essential Guide to Storing Website Files Efficiently
In today’s digital world, a fast, secure, and well-organized website is critical to online success. Whether you’re a web developer, digital marketer, small business owner, or blogger, understanding how to store website files efficiently is key to maintaining performance, security, and scalability.
In this essential guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about organizing, storing, and managing website files the smart way. You’ll learn best practices, discover common pitfalls to avoid, and gain expert tips to future-proof your web assets.
Why Efficient Website File Storage Matters
Before diving into the how-to, let’s talk about the why.
Efficient file storage affects:
-
Website speed: Poorly managed files can slow down load times.
-
Security: Misplaced or unprotected files can become security risks.
-
SEO: Search engines favor fast-loading, well-structured websites.
-
Scalability: Organized storage systems make it easier to scale your site.
-
Maintenance: Easy-to-navigate file structures save time during updates and troubleshooting.
Let’s get into how to make your website file storage efficient and sustainable.
Step-by-Step Guide to Storing Website Files Efficiently
1. Understand the Types of Website Files
Start by knowing what you’re working with. Website files generally fall into a few categories:
-
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files: These form the structure and behavior of your site.
-
Media files: Images, videos, and audio that enhance content.
-
Fonts and icons: Design elements that add style and branding.
-
Configuration files:
.htaccess,robots.txt, and.envfor server rules and environment settings. -
Database files: If using a CMS like WordPress, your site likely relies on a MySQL or MariaDB database.
Knowing the file types helps you plan where and how to store them.
2. Use a Logical Folder Structure
Tips:
-
Keep naming conventions consistent (use lowercase and dashes).
-
Avoid long or ambiguous file names.
-
Separate media types (e.g., don’t mix images and videos in the same folder).
3. Optimize and Compress Files
Large files slow down your site. Here’s how to keep things lean:
-
Images: Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim.
-
Code files: Minify CSS, JS, and HTML with tools like UglifyJS or CleanCSS.
-
Videos: Host large videos externally (e.g., YouTube, Vimeo) and embed them.
-
Fonts: Include only the necessary font weights and styles.
File compression improves load times and user experience — both important for SEO.

4. Use Version Control Systems
If you’re collaborating with others or managing regular updates, a version control system like Git is invaluable.
-
Keeps track of changes.
-
Makes collaboration seamless.
-
Allows rollback to previous versions.
Store your codebase in repositories (e.g., GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket) and avoid making live changes directly to the production server.
5. Leverage a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN stores copies of your files on servers around the world, delivering them to users from the closest location.
Benefits:
-
Faster load times for global users.
-
Reduced bandwidth on your main server.
-
Improved redundancy and uptime.
Popular CDNs include Cloudflare, Amazon CloudFront, and KeyCDN.
6. Secure Your File Directories
Security should never be an afterthought. Follow these best practices:
-
Use
.htaccessto restrict access to sensitive files. -
Set correct file permissions (e.g., 644 for files, 755 for directories).
-
Disable directory browsing to prevent outsiders from seeing file structures.
-
Regular backups: Store backups offsite (cloud or physical external drive).
Secure file storage not only protects your site — it builds trust with visitors.
7. Automate File Management Tasks
Why do manual work when automation can handle it for you?
-
Auto-backups: Use plugins or cron jobs to schedule regular backups.
-
Sync tools: Use Dropbox, Google Drive, or OneDrive to sync development files.
-
Image optimization plugins (for WordPress): Smush, ShortPixel, etc.
These tools save time and reduce human error.
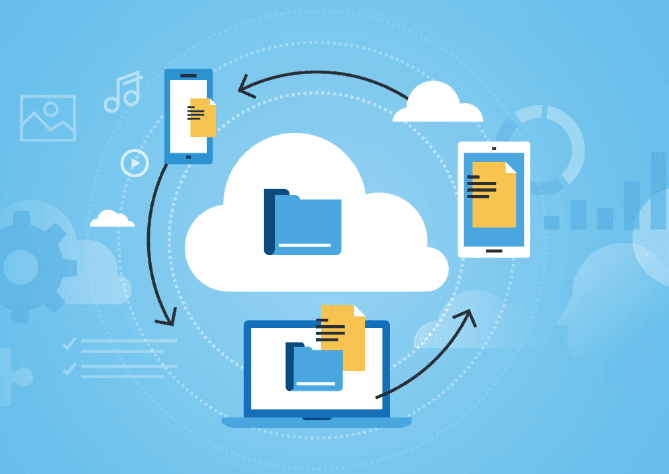
8. Use Cloud Storage Services Wisely
For media-heavy sites or collaborative projects, cloud storage solutions like Google Cloud Storage, Amazon S3, or Dropbox Business offer:
-
Scalability
-
High uptime
-
Easy sharing and access controls
Make sure to set proper permissions and automate backups when using cloud storage.
FAQs About Storing Website Files Efficiently
Q1: Should I store all files on the same server as my website?
Not necessarily. While it’s convenient, it’s not always the most efficient. Offloading media files to a CDN or cloud storage can dramatically improve performance.
Q2: What’s the best way to store backups?
Use both local and offsite backups. Services like UpdraftPlus (for WordPress) or tools like Rsync with cron jobs can automate this process.
Q3: How do I keep my folder structure organized over time?
Schedule periodic audits to delete unused files, rename confusing items, and archive older content. Consistency is key.
Q4: What’s the safest way to manage sensitive files like .env or config.php?
-
Don’t upload them to public directories.
-
Use
.gitignoreto exclude them from version control. -
Apply proper file permissions and restrict access via
.htaccess.
Q5: Can I use Google Drive or Dropbox to host website files?
These platforms aren’t designed for hosting public website content. However, they’re excellent for backups, team sharing, or version history.
Pro Tips for Long-Term Success
-
Document your structure: Keep a shared doc for your team explaining your file structure and naming conventions.
-
Monitor storage usage: Regularly check storage limits and usage stats.
-
Integrate with CI/CD tools: Automate testing and deployment of file changes for smoother updates.
-
Use relative paths: Avoid hardcoding URLs; relative paths are more portable across environments.
Conclusion
Storing website files efficiently isn’t just about tidiness — it’s about performance, security, and scalability. With the right structure, tools, and practices, your site will be faster, safer, and easier to manage.
From using CDNs and version control to organizing folders and optimizing media, every step you take improves your website’s health and future-readiness.
Whether you’re launching a simple blog or managing a high-traffic e-commerce platform, follow this essential guide to keep your website files clean, efficient, and under control.